Background:
Efficient operations at industrial plants require precise control of process temperatures. Wide-ranging ambient temperatures create operational problems in controlling these temperatures. To manage process temperature, operators utilize heat traces on process piping. Heat traces are controlled and monitored by heat trace controllers.
Heat trace controllers play a critical role in industrial systems by ensuring temperature control of process lines, maintaining process stability and integrity, and freeze prevention. Plant operators will monitor heat trace controllers by running a communication cable to the DCS or monitor them manually if they are not connected.
Challenge:
Refineries and chemical plants typically have numerous heat trace controllers throughout their plant, some connected to the DCS but often times many are left unconnected due to the high cost of running cabling. To ensure system integrity, local monitoring of the unconnected heat trace controllers is done several times daily, requiring manpower and exposure to the risks of hazardous area work and cold temperatures in the winter.
Solution:
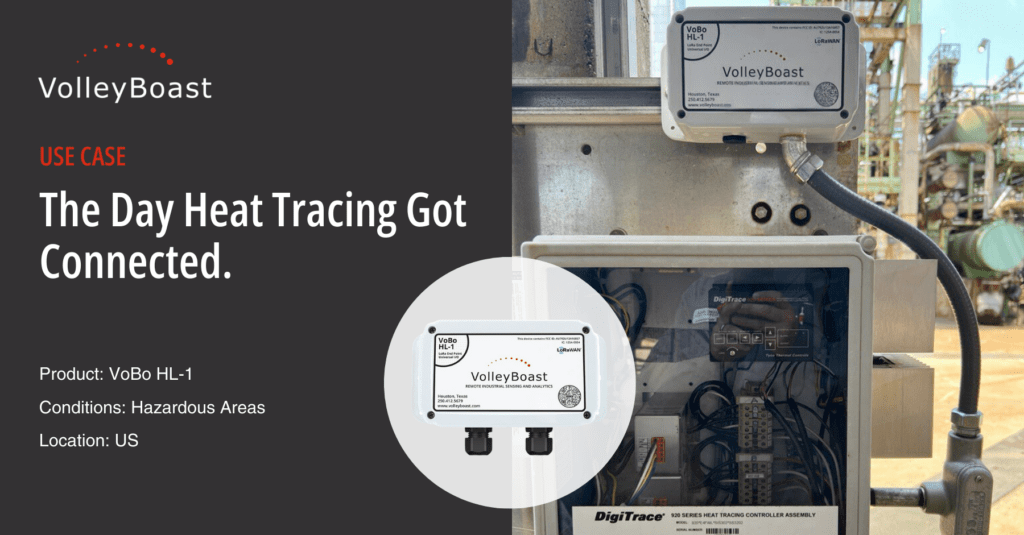
Volley Boast’s VoBo HL-1 is a LoRaWAN® bridge endpoint that provides a cost-effective way to retrieve data from existing unconnected systems or new installations. The VoBo HL-1 is a sensor-agnostic, multiple input channel, battery-powered solution certified for use in Class 1 Division 2 hazardous areas. In this case, the RS485 serial channel of the VoBo HL-1 is used to collect data from the heat trace controller and transmit it to the refinery’s LoRaWAN® network. The VoBo HL-1 is a Modbus master and reads the Modbus registers on the heat trace controller, sending the data to their monitoring system on a 30-minute cycle.
Results:
The plant’s DCS receives automatic updates on the performance of heat trace controllers every 30 minutes. If intervention is needed it can be done in near real-time, instead of reacting to data that can be 12 hours old.
Data collection utilizing the VoBo HL-1 and LoRaWAN wireless data transmission results in better control of process conditions, improved efficiency, time and money savings, and reduced risk to personnel.